What Is Diphtheria? Symptoms And Treatment
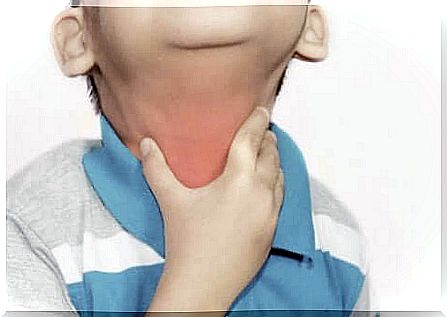
Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae . Although it is a fairly contagious disease, it is not very common in developed countries, as there is a vaccine that effectively prevents it.
This disease tends to spread in areas where people are not vaccinated.
Symptoms of diphtheria
Many people who are infected with diphtheria do not show strong symptoms. In some cases, however, the disease can lead to death.
The disease produces a variety of toxins that enter the bloodstream. From there, they reach the heart, brain and other organs and cause serious organ damage.
These are some common symptoms of diphtheria:
- Blocked airways
- Swollen throat
- Fever
- Overindulge
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Snoring
- Hard to breathe
- Difficult to swallow
- Wheezing
- A grayish, thick coating in the throat
- Infection of the mucous membranes of the nose
Complications related to diphtheria
The disease has an incubation period of 2 to 5 days and usually affects the patient’s vital organs. Therefore, it is extremely important to be aware of symptoms that may indicate that someone has been infected.
Below is a list of the complications that can occur if you do not treat the disease in time.
Damage to the nervous system
When a disease affects the nerves, this can lead to muscle paralysis, which can make it difficult to walk, swallow and even speak.
In the worst case, you die of diphtheria if you do not get medical help as a result of paralysis of the respiratory system.
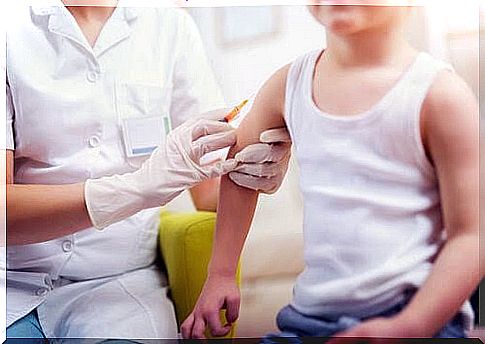
Damage to the heart
As I said, the disease produces toxins that enter the bloodstream and affect the vital organs, including the heart.
Diphtheria can inflame the heart muscle, which can lead to heart attack. Fatigue and palpitations are signs of damage to the heart from the toxins.
Treatment of diphtheria
As soon as you suspect the disease, it is important that you seek immediate treatment. This applies even if the diagnosis is not definitive. Treatment for diphtheria requires hospitalization.
At the same time, it is important to isolate the patient given how contagious the disease is. In very sensitive cases, the victim must be cared for in an intensive care unit.
Treatment involves the following:
Antibiotics
Antibiotics eliminate the bacteria present in the body. This reduces the disease’s ability to continue to spread in the body and to other people just as easily.
The most common antibiotics used to treat diphtheria are penicillin and erythromycin.
Antitoxins
Doctors administer an intravenous or intramuscular antitoxin, or antidote. By doing this, they neutralize the development of the infection through the bloodstream and prevent it from reaching the patient’s organs.
Antitoxins can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, which means that doctors must first perform a skin allergy test before administering the antidote.

How to prevent diphtheria
Vaccine against diphtheria is included in the general vaccination program. It consists of an inactive toxin that does not damage the organs. It produces antibodies that can neutralize the diphtheria bacteria. This vaccine effectively prevents the disease.
For the vaccine to work, a child must receive 5 doses.
However, adults must receive 10 doses of the vaccine for it to be effective. People who are going to travel to an area with an increased risk of this disease should also receive an extra booster dose. The same applies to people who have had contact with someone who has the disease.
This extra precaution does not apply to those who have been vaccinated in the last five years.
Diphtheria in the skin
The disease can also affect the skin and cause reactions that include redness, pain and swelling. At the same time, it can lead to wounds being covered with a grayish film.
As with diphtheria that affects the airways, it is also more common to get an infection in the skin in tropical regions. It is more common for people to get skin diphtheria if they live in cramped conditions.
This is a low-risk disease given the presence of a preventive vaccine. Despite this, it is important to learn about the disease because it spreads easily and is common in tropical areas. Prevention and early detection are the key to avoiding complications.