Oral Candidiasis In Children: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment

Oral candidiasis in children – or cod – is a common infection of the oral cavity due to an overgrowth of candida fungi, the most common being candida albicans. The incidence varies depending on age and certain predisposing factors. It usually affects children under 6 months and newborns.
Causes of oral candidiasis in children
Some microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, etc.) live regularly in the body. Some of them are harmless, but others can trigger an infection.
As the immune system in children and infants has not yet fully developed, they are more likely to become infected with fungi that live regularly in the body. Risk factors include the following:
- Impaired function in the salivary gland
- Medication (certain antibiotics or corticosteroids)
- Prostheses
- High carbohydrate diet during extreme life situations
- Smoking
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Malignant neoplasms
- Immunosuppressive conditions in the elderly and newborns
Classification of candidiasis
When the yeast candida albicans develops and spreads too much in the oral cavity, we often call the outbreak “cod”. According to studies published in dermatological therapy , the classification of oral candidiasis by evolution or location is as follows:
- Acute candidiasis: Is divided into pseudomembranous and erythematous forms
- Chronic candidiasis: Pseudomembranous, erythematous (atrophic) and hyperplastic form
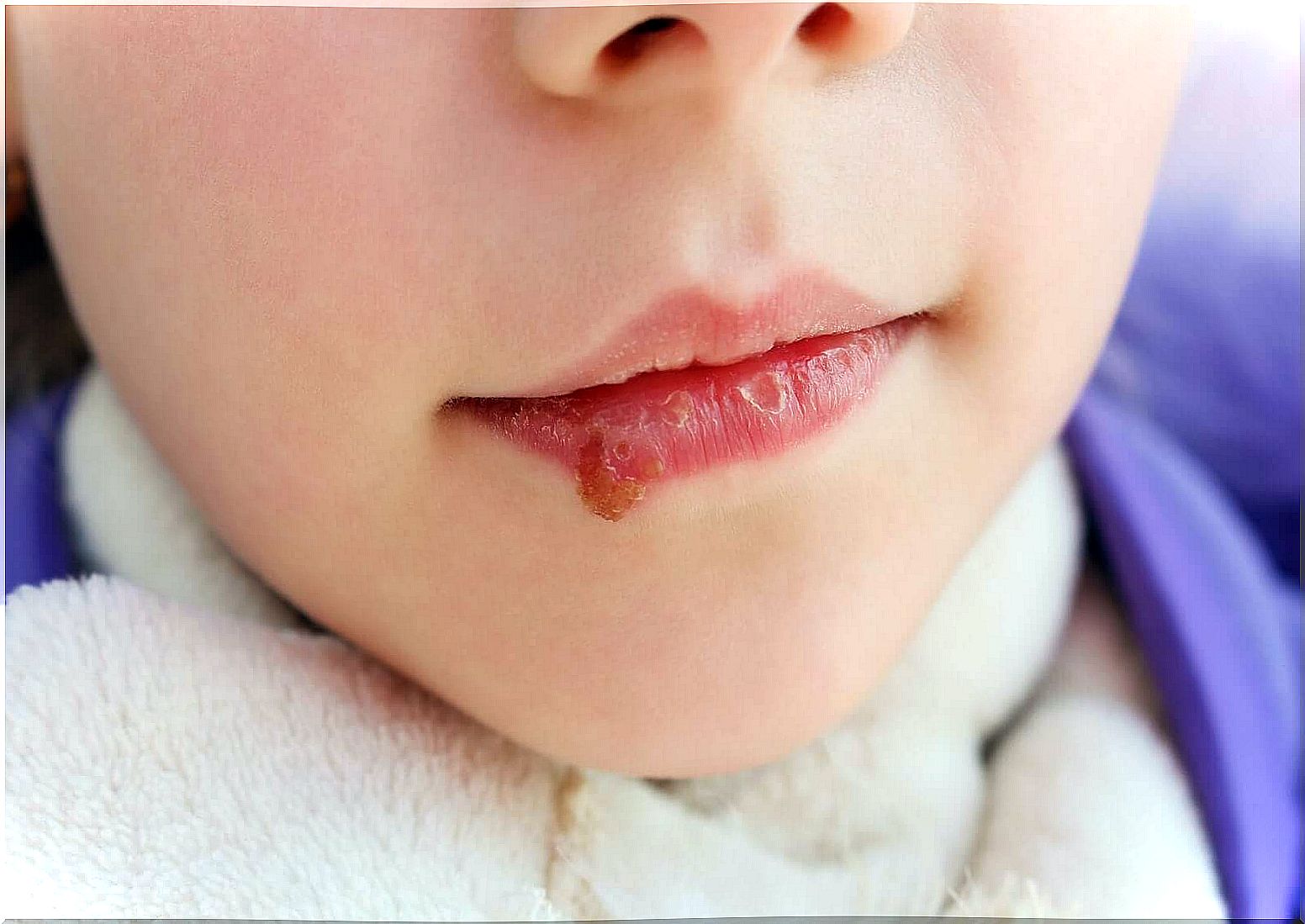
- Angled cheilitis: Or infectious angular cheilitis, which is cold sores in the mouth pores
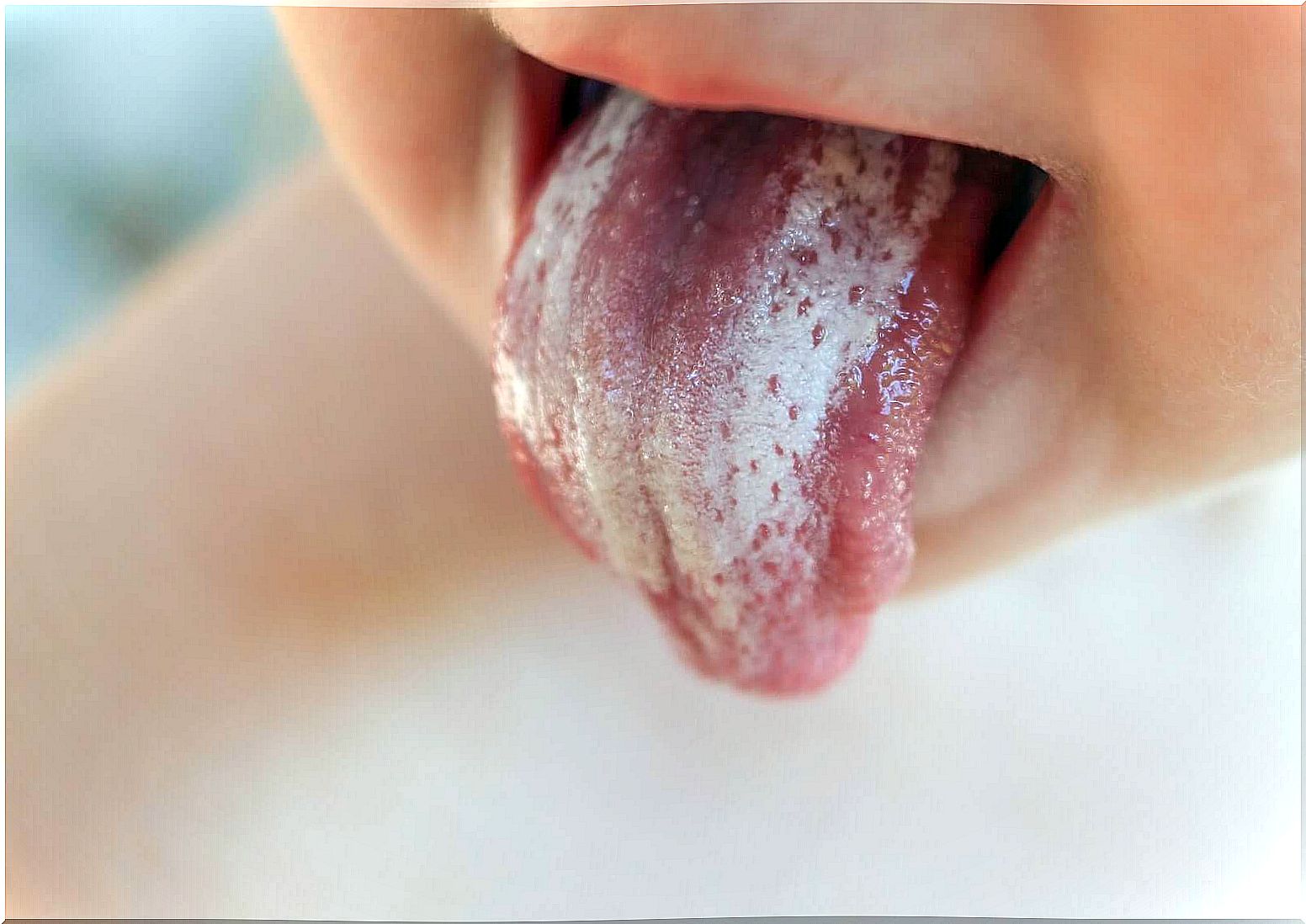
Symptoms and signs of oral candidiasis
The clinical picture that candida infections trigger may be similar to other health problems. Symptoms of cod include the following:
- Odynophagy (sore throat)
- Dysphagia (pain when swallowing)
- Halitos or loss of taste and appetite
- Bleeding when rubbing the rash
- White, velvety slag on tongue and mouth
There are usually no symptoms of general discomfort. In fact, in some cases there are no symptoms or the rash is painless.
Diagnosis of candidiasis in children
A medical specialist will perform the diagnosis of candidiasis in children. Here, care staff will interview the child or mother to investigate possible predisposing factors and health history. The clinical results of the patient will complement the answers to the questions and both will help to make a definitive diagnosis.
In cases where there is some doubt at the time of making and defining a diagnosis, the doctor may perform a scraping of the secretion to analyze under a microscope. There are even more serious cases where candidiasis spreads to the esophagus. Consequently, the physician must create a culture of the affected tissue to study the microbe that produced it.
What are the therapeutic options?
An important part of the treatment of candidiasis in children is proper mouthwash. This means that patients who are in good health will recover more easily than those who have an underlying disease.
Fungicides are the drugs used to treat candidiasis. The specific type of fungicide will also depend on the site of the rash in the body (nystatin, clotrimazole, fluconazole, miconazole, amphotericin B).
In mild cases of oral candidiasis in children, doctors prescribe appropriate oral medication, whether tablets, pills or capsules. In turn , children should consume yogurt or eat probiotics such as Lactobacillus that reduce the growth of candida albicans and prevent infections, according to studies published in the medical journal Micosis .
Tips to prevent future outbreaks of candidiasis
It is important to know that there is a high probability of future outbreaks of candidiasis if the cause was not remedied correctly and effectively. Therefore, the best way to treat cod and prevent recurrent infections is to address the underlying cause.
Some of the following recommendations help to avoid new outbreaks over time:
- Maintain proper oral hygiene: Do not divide toothbrushes and replace them regularly. Perform proper oral hygiene every day.
- Disinfect objects: Disinfect bottles, pacifiers and utensils commonly used by infants and children.
- Mouthwashes: Perform mouthwashes to ensure the cleanliness of the oral cavity. One of the options for this is with mouthwash with warm saline.
Prognosis for oral candidiasis in children
As we have mentioned, candidiasis in children can develop without symptoms or signs. However, when damage is present and treatment begins, it usually disappears within 2 weeks. In children with weakened immune systems, however, treatment processes take longer and require more care.