Scabies In Children: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Scabies is a common and contagious skin disease in children. Although it can affect children of any socio-economic level, people living in poverty or in overcrowded conditions have a much higher risk of being affected. In addition, the risk of getting scabies is greater in young children, the elderly and people with weakened immune systems.
Causes of scabies in children
Scabies develops from mites, Sarcoptes scabiei , which spread via direct skin contact. If these mites are not in contact with skin, they can only survive for about 24 to 36 hours. Therefore, transmission through infectious objects such as clothing, sheets and blankets is limited.
The infected child develops a hypersensitivity reaction to the mites, their eggs and their feces. This reaction can occur three weeks after exposure to the infectious source.
In 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared scabies a neglected skin disease. For mites to spread between people, only 10 minutes of skin contact is needed.
Symptoms of scabies in children
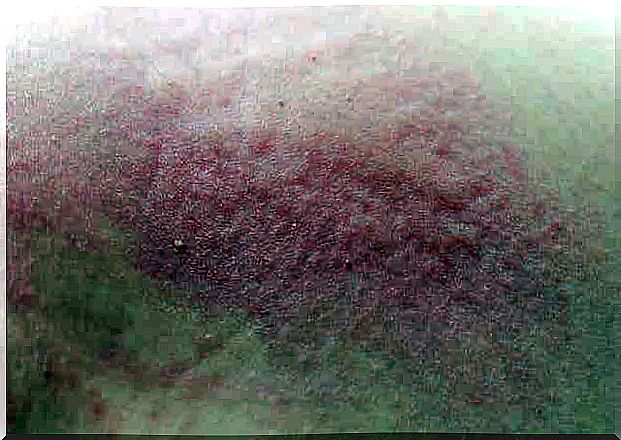
The symptoms of this parasitic infection include erythematous rash and a generalized itching, which usually increases at night. According to a publication from the Asturias Pediatric Society, lesions occur in children on the soles of the feet and soles of the feet. However, in adults, the occurrence of scabies varies and it can occur between the fingers, in the flexion of the wrist, elbows, armpits and at the genitals and breasts.
It takes about three weeks after contact with mites for all symptoms to occur. In the case of re-infections, however, clinical manifestations can occur within just a few hours after contact.
How to diagnose?
The basis for the diagnosis of scabies in children is a consultation and observation of the skin lesions by a dermatologist. The physician thoroughly reviews the patient’s medical history to rule out other causes. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor analyzes mites, eggs or feces from a skin scrape under a microscope.
If the dermatologist is not completely sure of the diagnosis, he or she can also take a biopsy of the lesion to diagnose scabies with certainty. However, this procedure is not very common.
Differential diagnostics
It is easy to confuse scabies with other itchy rashes:
- Eczema
- Swine pox
- Ringworm ( Tinea corporis )
- Prurigo nodularis
- Dermatitis
- Original pathologies
- Psoriasis
When it comes to scabies, it is actually possible to find the routes that mites take to move; these tunnels are called. These are white meandering lines that indicate that the parasites have been on the move.
Therapeutic options for scabies in children
To avoid transmission and re-infection, it is important to treat symptomatic or asymptomatic household members at the same time. The main reason for treating people without symptoms is that it can take several weeks before the symptoms actually appear.
Permethrin
A topical treatment for scabies is lotion or cream with 5% permethrin. You should apply the cream on the skin from the neck to the toes, usually at night; the next day you rinse it off.
For infants who have scabies, you should also apply the cream on the face. One week after the first application, you must repeat the procedure to kill all larvae born during this period. Patients and relatives should be informed of the high probability that itching will persist for a long time.
Ivermectin
Oral ivermectin is another option for treating scabies in children aged 10 years and up. Again, it requires an initial treatment followed by a second dose after one week. This therapeutic option may be preferred due to the following benefits:
- For its convenience, as it increases the compliance rate
- Security
- Easy administration, as it reduces the likelihood of abuse or misuse
- Get negative effects
- Other variants
In addition, you must disinfect sheets, blankets, towels and clothes. Another treatment option is precipitated sulfur (5%).
In the case of pregnant women and young children, you should use precipitated sulfur (5%) mixed with Vaseline. Although its odor and bumpy application make you want to avoid this treatment, this treatment is the safest option.
Eventually, symptoms and signs may persist for several weeks, even with proper treatment, before resolving completely. The good prognosis for the disease is related to the treatment of the patient and his or her close contacts. Therefore, if the treatment is not carried out properly, scabies can spread to the rest of the close contacts.